April - June, 2025 • Vol. 45 • # 2
Triglyceride-Glucose Index predicts type 2 diabetes risk and progression of diabetic nephropathy: a critical appraisal
The Triglyceride-Glucose (TyG) Index has emerged as a valuable marker in predicting the onset and progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and its associated complications.
RSSDI white paper on diabetes: current status, challenges, and future vision
India is currently facing a diabetes epidemic. Recent data from the ICMR-INDIAB study estimates that over 101 million Indians live with diabetes, with an additional 136 million in the prediabetes stage.
Rationality over convenience: The CDSCO’s regulatory ban on irrational antidiabetic fixed-dose combinations in India and its clinical- pharmacological imperatives
Fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) have become a mainstay in managing type 2 diabetes in India, offering potential benefits such as simplified regimens, improved adherence, and better glycemic control.
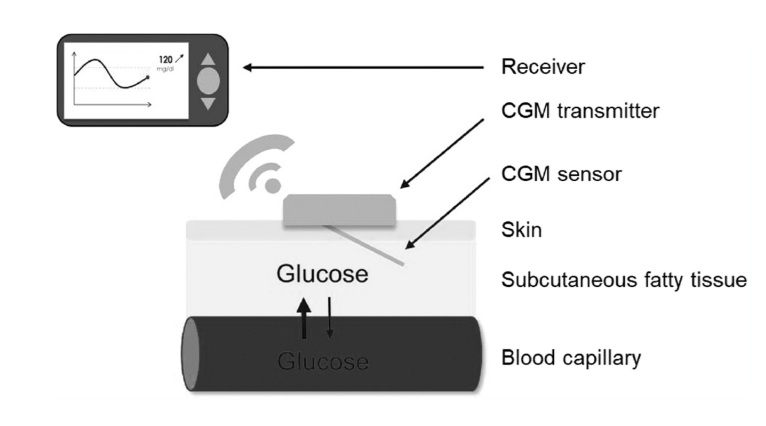
Continuous glucose monitoring data for artificial intelligence-based predictive glycemic event: A potential aspect for diabetic care
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects 537 million of the population worldwide whereby continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been implemented in the management of diabetes.
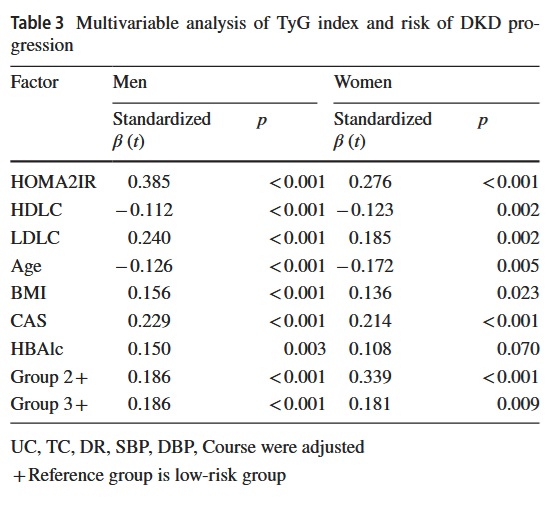
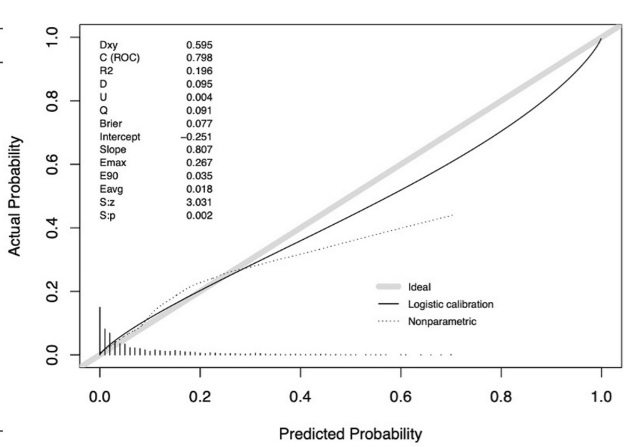
Associations between triglyceride-glucose index and risk of diabetic kidney disease progression in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Pending connections exist between the TyG index and the risk assessment of diabetic kidney disease (DKD), which includes glomerular filtration rate and urine albumin to creatinine ratio. DKD progression risk and the TyG index were examined in this study.
Safety and efficacy of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during fasting in the month of Ramadan: an experience from tertiary care hospital
The data regarding the safety and efficacy of dapagliflozin during fasting is lacking especially in Pakistan. So, the current study aimed to explore the safety and efficacy of dapagliflozin in minimizing the episodes of hypoglycemia during fasting and reducing the HbA1c.
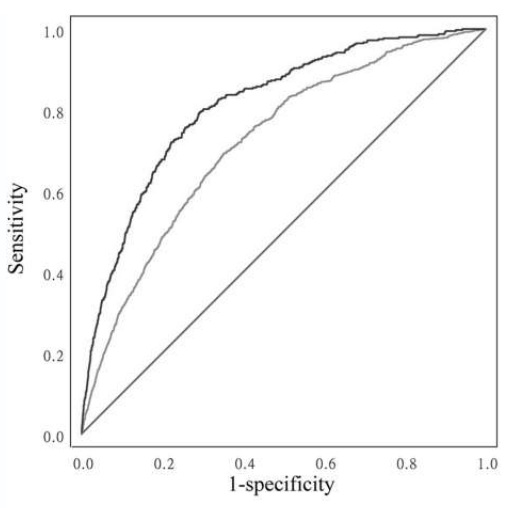
Gender differences in triglyceride glucose index predictive power for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Chinese cohort study
This study aims to explore the association between the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Chinese men and women while assessing its predictive capability by gender.
The association of fasting and postprandial GIP and glucagon levels with glycemic variability evaluated by flash glucose monitoring system in type 1 diabetes
This study is to explore the relationship between serum fasting and postprandial glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon levels and glycemic variability in type 1 diabetes (T1D).
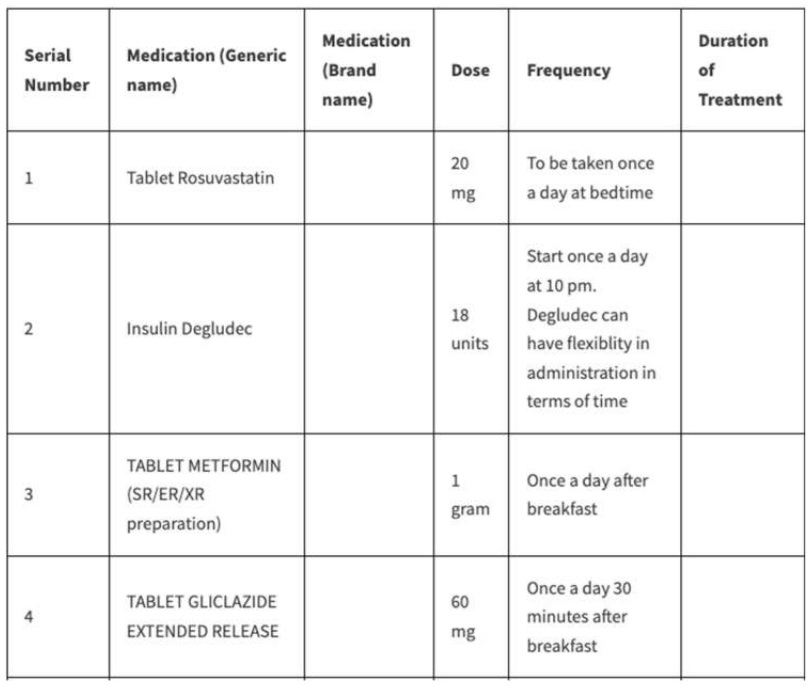
An alpha-test of Diabetology.co.in-an algorithm-driven personalized and precision medicine prescription system for treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes
This study evaluates Diabetology.co.in, an innovative algorithm-driven prescription system developed for personalized and precision treatment of treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. It focuses on integrating computational medicine with clinical practice, leveraging artificial intelligence for optimized diabetes management.
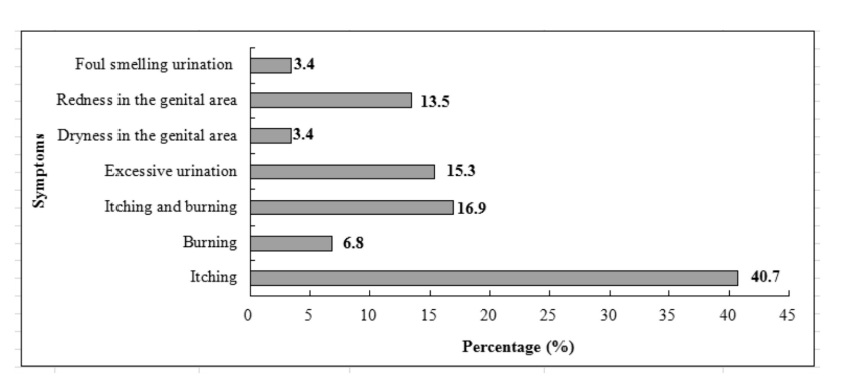
Prevalence of genitourinary symptoms in people with type 2 diabetes initiated with SGLT2 inhibitors
Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors prevent the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose from the urine. In addition to glucose-lowering effect, SGLT2 inhibitors can also reduce blood pressure and result in weight loss. In spite of the benefits of this drug, it predisposes patients to genitourinary tract infections.
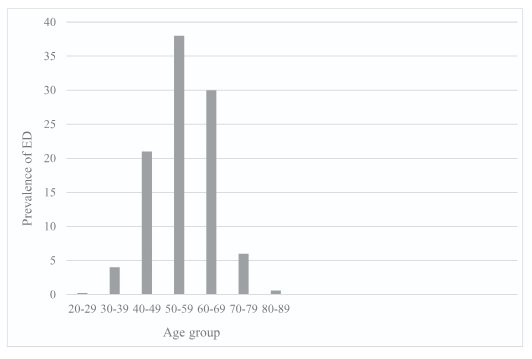
A retrospective study on the prevalence of erectile dysfunction among Indians with T2DM using single-question self-reporting method and its association with diabetes complications and CV risk factors
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent complication of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) globally. However, there are lack of comprehensive studies on the association of ED with DM comorbidities and complications, especially among the Indian population.
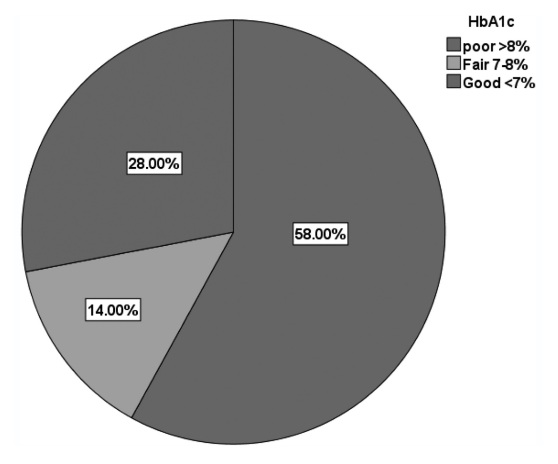
Prevalence and risk factors of poor glycemic control and diabetic nephropathy among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Dhamar, Yemen
Glycemic control is a significant step in reducing diabetic complications. The purpose of this study was to determine the prevalence and risk factors for poor glycemic control and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Dhamar, Yemen.
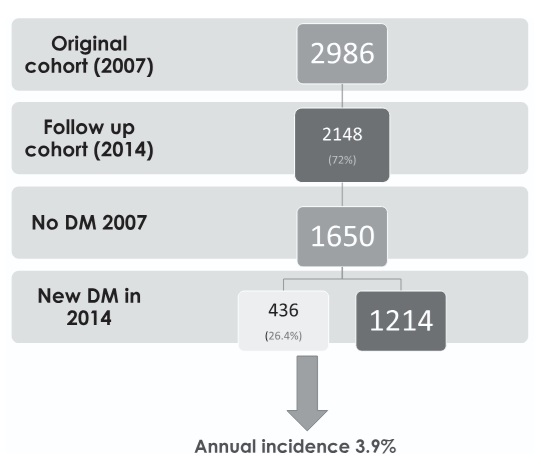
Incidence and predictors of diabetes mellitus: A 7- year community cohort follow-up of urban, adult Sri Lankans
There is limited data on the prevalence and outcome of prediabetes and the incidence of type 2 diabetes in South Asia.
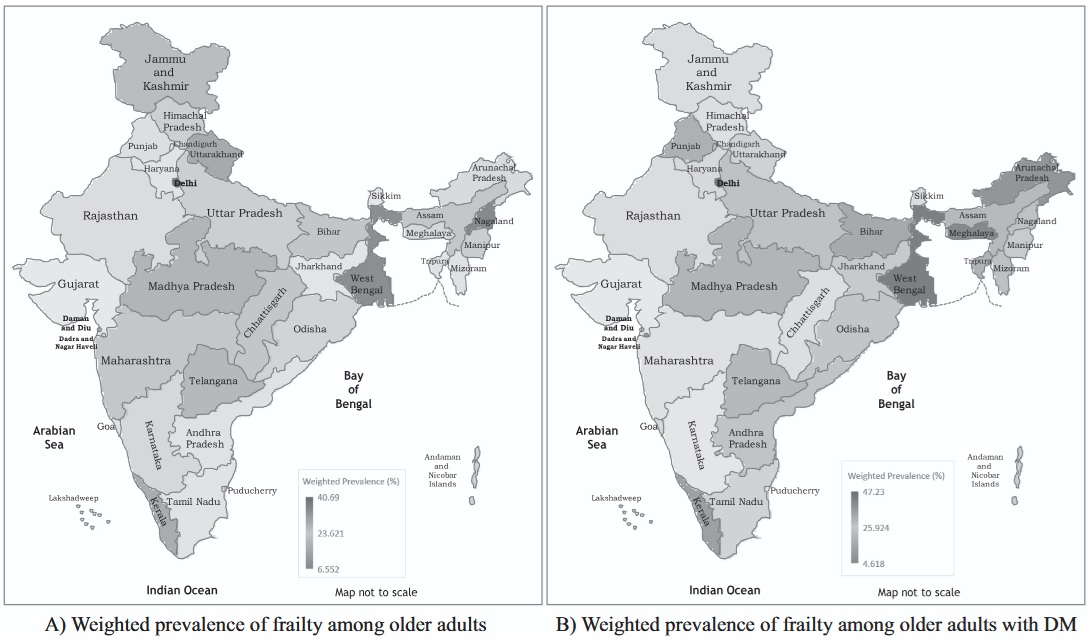
Diabetes and frailty in community dwelling older adults in India: insights from the longitudinal aging study in India
The study objective was to determine the prevalence and determinants of frailty among older individuals with DM in India. We also examined the relationship between DM, frailty, and food insecurity.
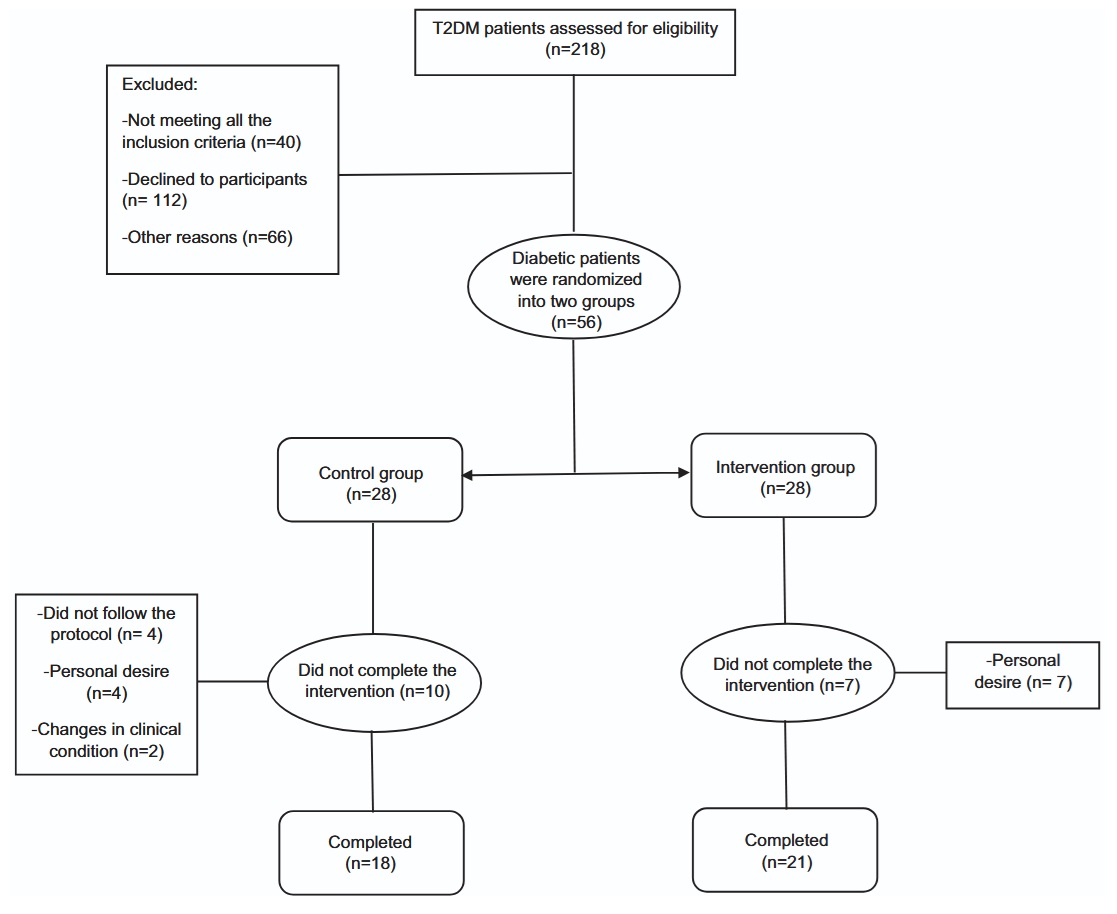
The effect of oral consumption of sesame oil on anthropometric, metabolic and oxidative stress markers of patients with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial
Sesame oil has several polyphenols with possible anti-diabetic and antioxidative characteristics. However, there is limited evidence for the efficacy of sesame oil on type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) consequences
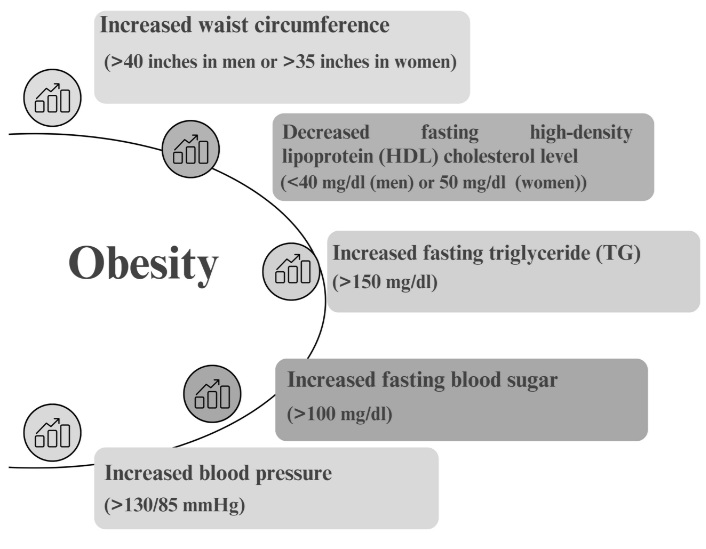
Herbal tea used globally targeting metabolic syndrome: A systematic review
Metabolic syndrome (MetSyn) is a cluster of metabolic constellations which includes hypertension, central obesity, insulin resistance and atherogenic dyslipidaemia. MetSyn is a group of interconnected risk factors linked to diabetes, cancer, stroke and other comorbidities.
Hormone imbalances detected in study participants with pre-diabetes in a Durban-based clinical setting, South Africa
Type II diabetes mellitus onset is linked with hormonal imbalances. However, the knowledge about hormonal alterations in pre-diabetes is limited.
Healthy lifestyle index development and its association with type 2 diabetes mellitus status among teachers
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a significant health concern and imposes a substantial burden on society. Although leading a healthy lifestyle is an effective means of reducing the risk of T2DM, the complex interplay of diverse lifestyle factors necessitates a comprehensive assessment.
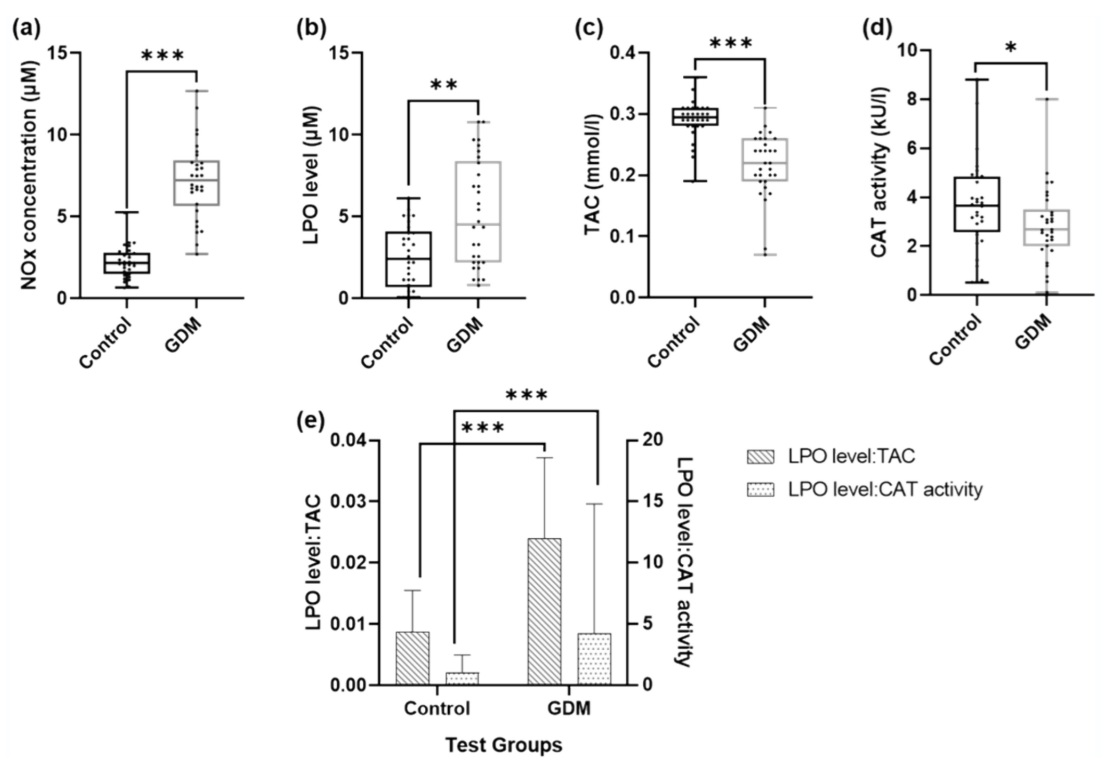
A Sri Lankan pilot case-control study on gestational diabetes mellitus: oxidative stress and a potential diagnostic marker panel
Oxidative stress is suggested as a potential contributary factor for feto-maternal complications in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and the understanding of oxidative stress and antioxidant levels in GDM still remains obscure.
Assessment of Quality of Life in Urban Indian Population with Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension
Diabetes mellitus and hypertension have a high prevalence of non-communicable diseases threatening the world. In such a case, the quality of life of these patients is of utmost importance.
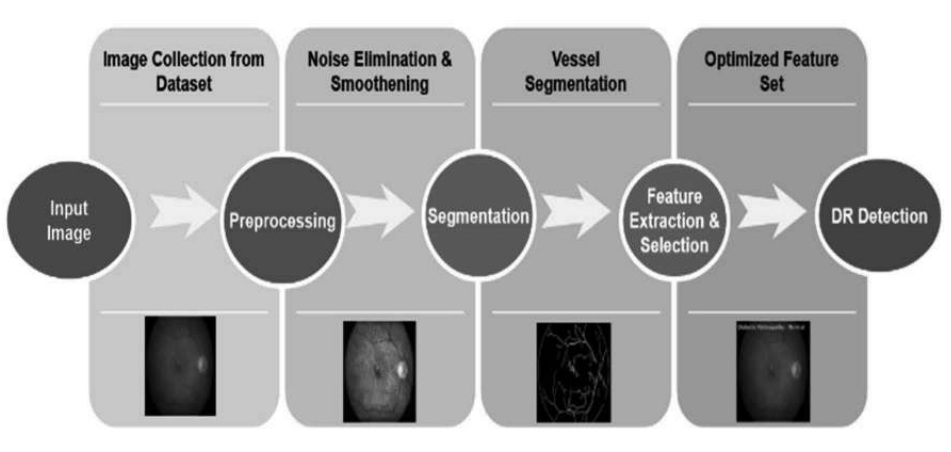
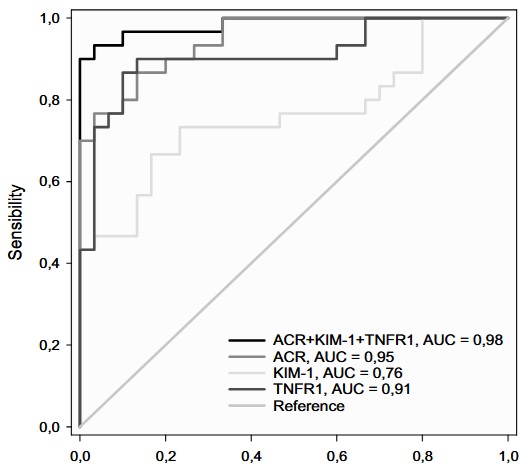
Optimized multiparametric approach for early detection of kidney disease in diabetic patients
Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) is a serious complication of diabetes. Identifying high-risk DKD patients can lead to better clinical outcomes.
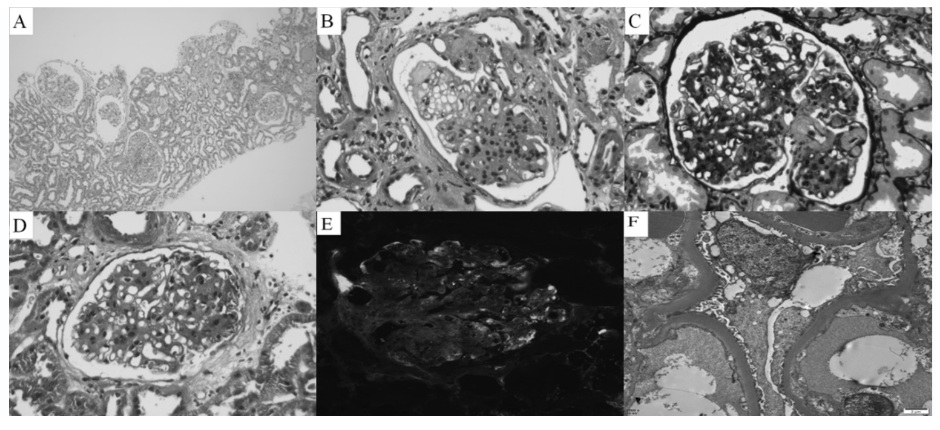
Unusual phenotypes of diabetic nephropathy: A case report
The prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus (DM) are rapidly increasing worldwide. Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a chronic complication of DM and major cause of end-stage renal disease.
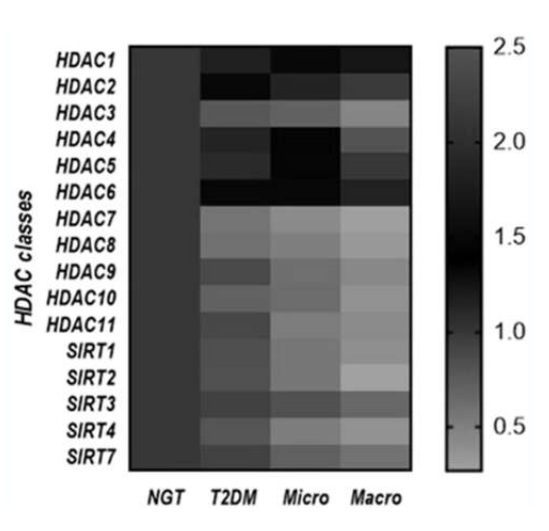
Comprehensive gene expression analysis of histone deacetylases and the transcription factor Nrf2 in the progression of diabetic nephropathy
Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a crucial transcription factor in maintaining cellular homeostasis. The regulation of Nrf2 expression is an essential target for treating diabetic nephropathy (DN), and this regulation has been reported to be influenced by epigenetics.
The effect of 8 weeks of endurance and resistance exercises on the serum levels of FGF23 and s-Klotho in type 2 diabetic women
We evaluated the effects of 8 weeks of endurance and resistance training on serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), soluble klotho (s-Klotho), 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (VitD), and diabetes biomarkers in overweight/obese postmenopausal type 2 diabetic (T2DM) women
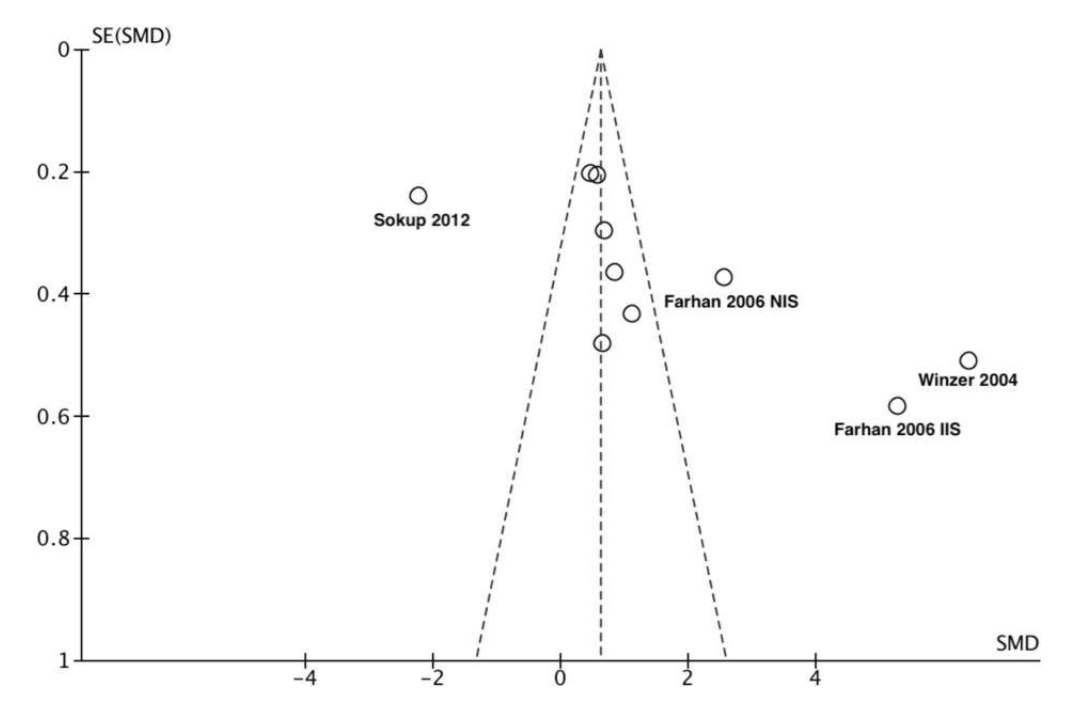
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels in prior gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Conflicting results on the association of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) with prior gestational diabetes mellitus (pGDM) have been observed among studies that imply the need to perform a meta-analysis.
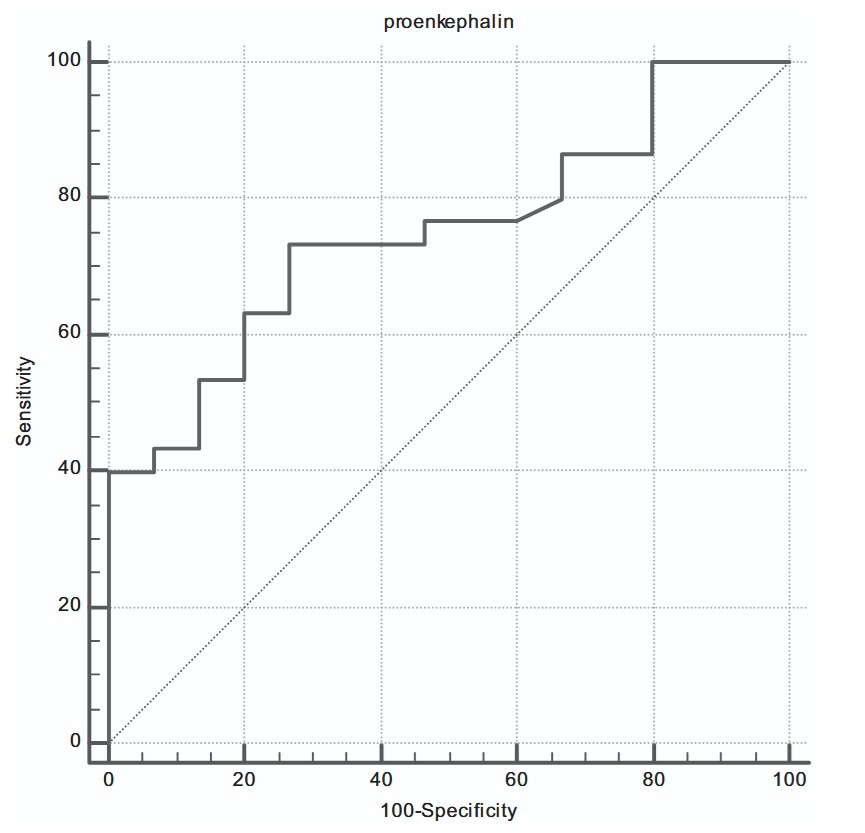
Role of stanniocalcin-1 and proenkephalin-A as novel biomarkers in prediction of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that carries substantial implications for health, social well- being, and economic factors. Stanniocalcin-1 STC-1 is a polypeptide hormone that was initially distinguished as a controller of calcium/phosphate homeostasis in the fish.
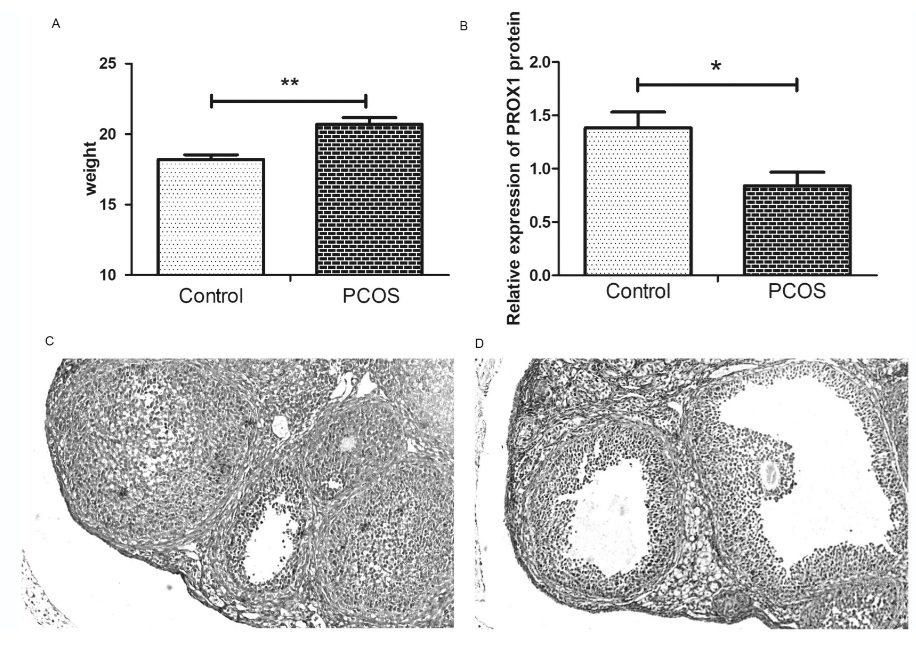
Novel pleiotropic variants associated with type 2 diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome detected using a pleiotropic cFDR method
Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) on polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) are usually conducted as single trait, rather than a simultaneous analysis of the related traits. Therefore, the overlapping genetic mechanisms underlying those traits were largely unknown.