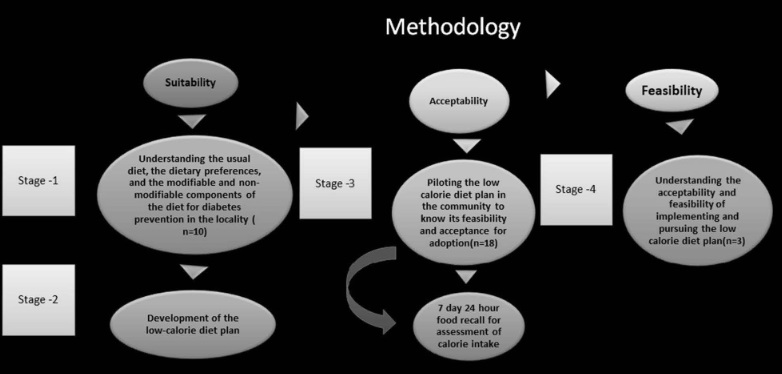
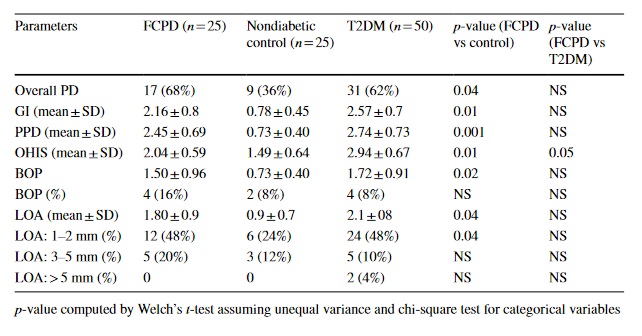
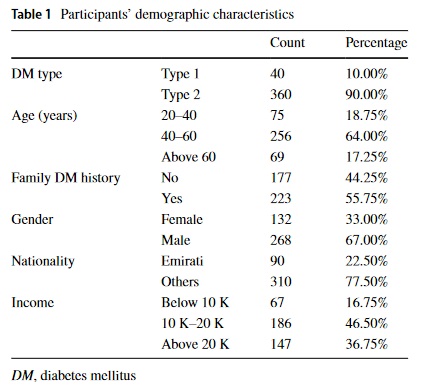
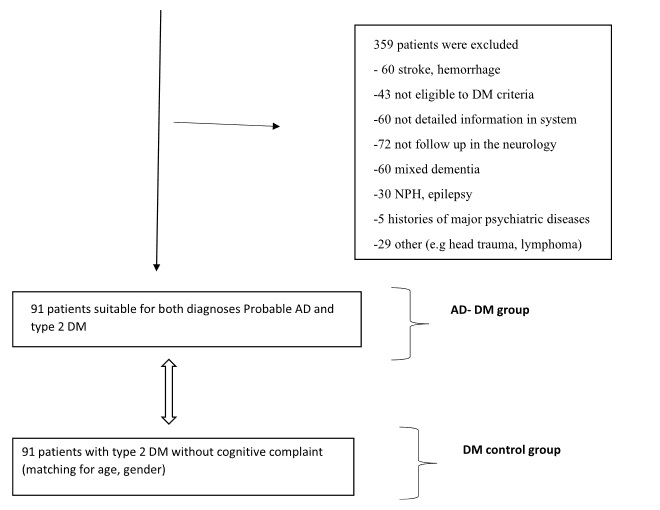
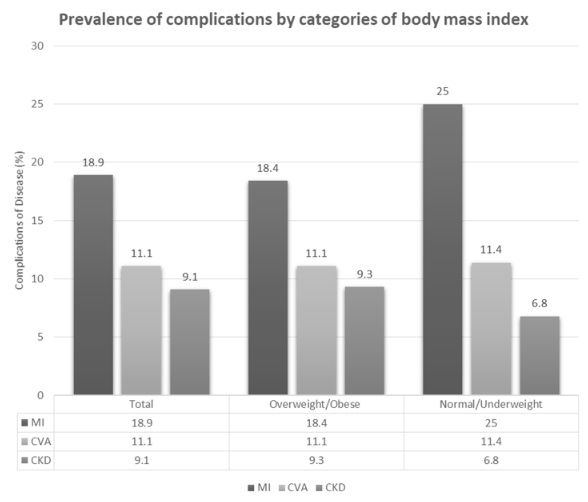
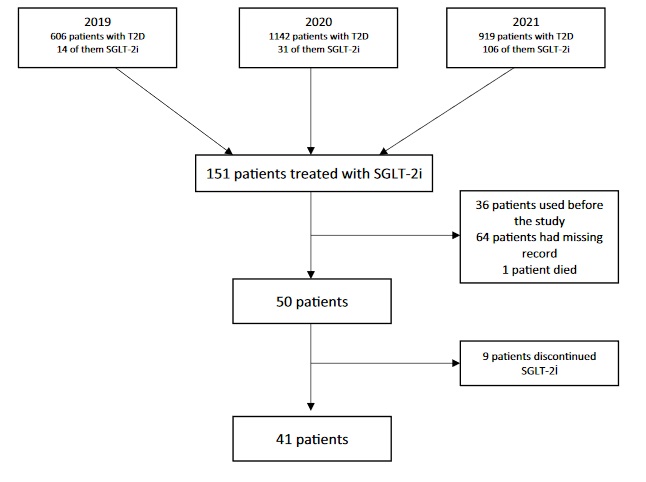
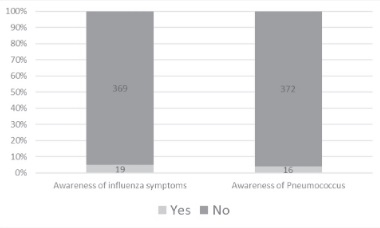
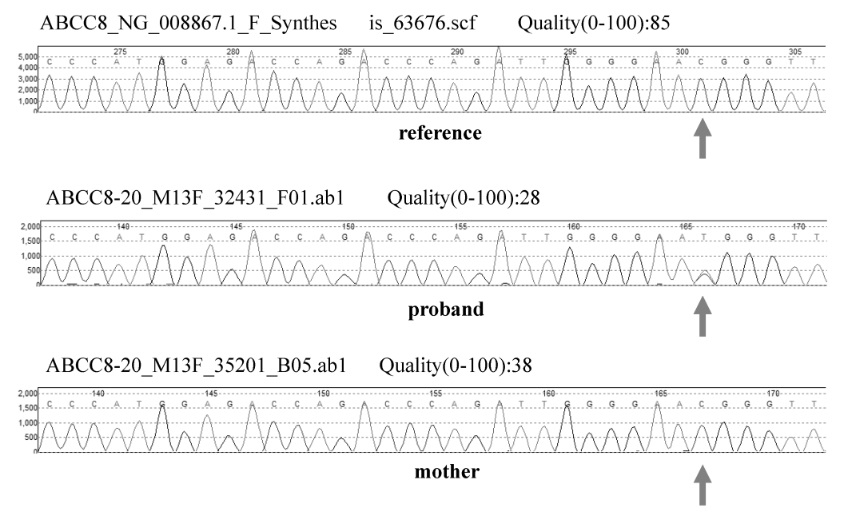
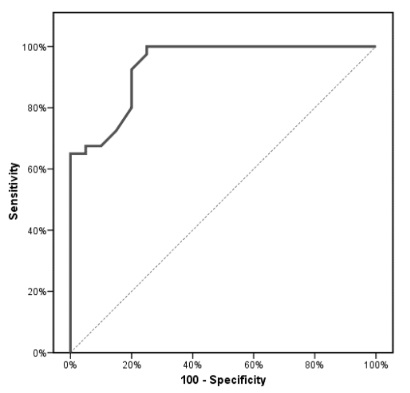
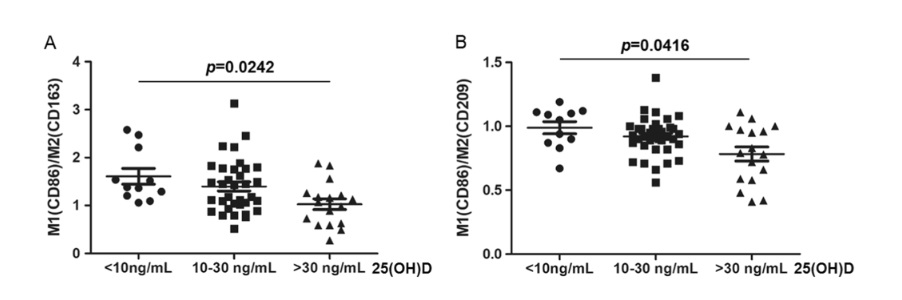
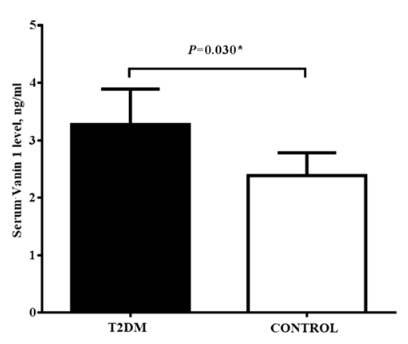
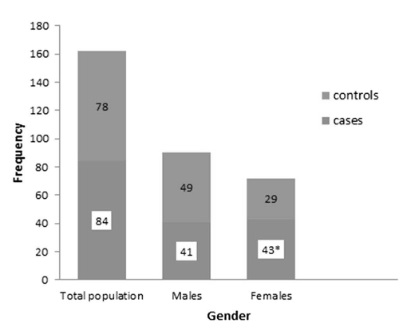
Screen for DPN-save limbs and lives!
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most common causes of neuropathy worldwide. Prevalence of PN in patients with diabetes (diabetic peripheral neuropathy) ranges from around 10.5 to 32.2% in various studies across India, and up to 50% patients will eventually develop neuropathy during the course of their disease according to Western literature. There is much higher prevalence of DM in India compared to the West.