July-September, 2024 • Vol. 44 • # 3
Diabetes and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, CVD: a continuum
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has emerged as the predominant chronic liver condition worldwide, affecting an estimated 38% of the global adult population.
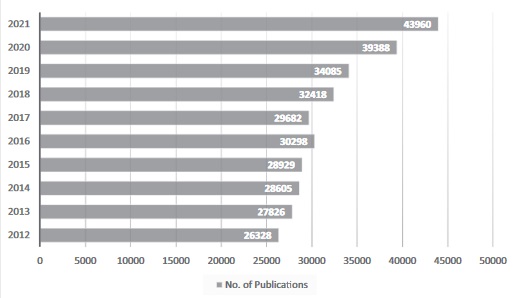
Global trend of research and publications in endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism: 1996-2021
Diabetes and related metabolic syndromes represent a significant global health challenge, with the global burden of diabetes increasing considerably since 1990. In this article, we examined the trend of publications in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism between 1996 and 2021, focusing on Asian countries.
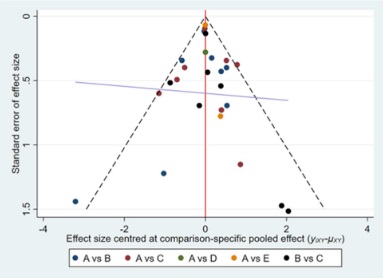
Effects of novel glucose-lowering drugs on the COVID‑19 patients with diabetes: A network meta-analysis of clinical outcomes
This study aimed to assess the effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter inhibitors (SGLT2i), glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i) on individuals subjected to diabetes and COVID-19.
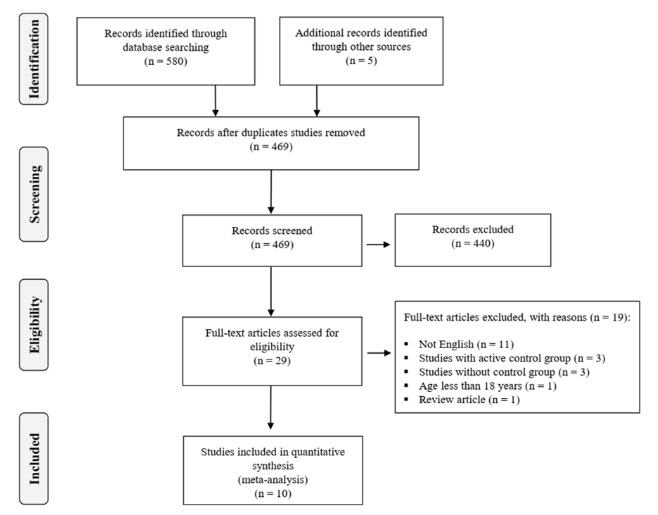
The effect of exercise training on serum Omentin-1 levels, glycemic control and body composition in adults population: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Omentin-1 has been acknowledged as an anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing marker, which is mainly expressed in adipose tissue. Exercise training is a therapeutic intervention that can possibly improve and modify circulating Omentin-1 levels.
Surrogate markers of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in children and young adults with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review & meta-analysis (MetS and IR in T1DM)
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) and insulin resistance (IR) are associated with diabetes. Insulin therapy in type 1 diabetes (T1DM) may complicate the diagnosis of both these conditions. Therefore, investigation of the diagnostic efficacy of MetS and IR components is important in paediatric population with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).
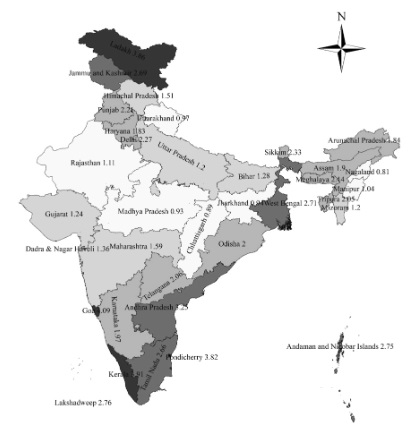
Bio-demographical determinants of diabetes among women in reproductive age group (15-49) in India: Evidence from National Family Health Survey (NFHS) of India, 2019-2021
Diabetes is a non-communicable disease, and the prevalence of diabetes is higher in low and middle-income coun- tries. In India, diabetes prevalence has been observed, with some regional variations across the states. This study analyses the current scenario of diabetes in India among women of the reproductive age group between 15 to 49 years.
The effect of dapagliflozin use on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients hospitalized with COVID-19
We aimed to evaluate the impact of dapagliflozin on reducing major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and all-cause mortality in patients with COVID-19 and to assess whether it was associated with clinical improvement
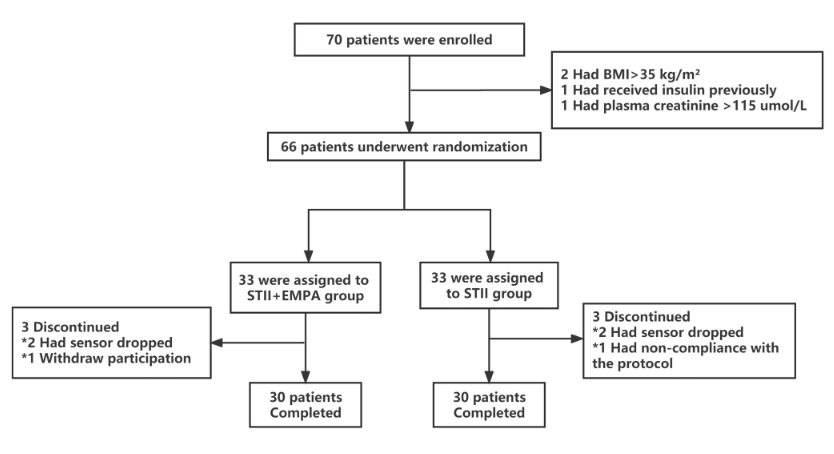
Empaglifl ozin combined with short-term intensive insulin therapy improves glycemic variability and 1,5-anhydroglucitol in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial
We aimed to compare glycemic variability (GV) parameters using both a flash glucose monitoring (FGM) system and cardiometabolic risk parameters in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) between cohorts receiving short-term intensive insulin infusion (STII) plus empagliflozin (EMPA) combination therapy vs. STII therapy alone.
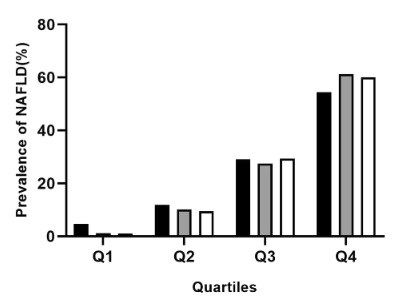
Correlation between triglyceride-glucose index and related parameters and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in northwest China
The triglyceride glucose (TyG) index and obesity are significantly closely related to the incidence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The study aimed to investigate the relationship among the TyG index and its related parameters [TyG-waist circumference (WC) and TyG-body mass index (BMI)] with NAFLD
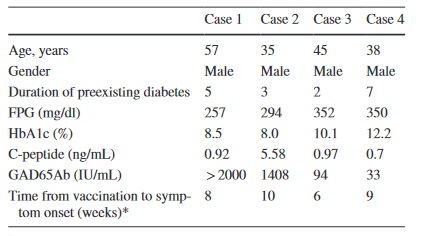
Diagnosis of latent autoimmune diabetes after SARS–Cov2 vaccination in adult patients previously diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Acute worsening of glycemic control in diabetic patients and new–onset type I diabetes were reported after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccines. Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) is defined as a slowly evolving immune-mediated diabetes. A few cases of LADA diagnosed after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination have been reported in the literature. This study aims to report LADA after mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations in subjects with a history of well-controlled type 2 diabetes.
Association between dietary glycemic and insulin index/load and cardiometabolic risk factors among people with diabetes
Limited studies have been conducted on insulin index/load, with inconsistent results regarding the glycemic index/load in relation to cardiometabolic risk factors among people with diabetes. The present study aimed to reveal the association of dietary glycemic index and load and dietary insulin index and load with cardiometabolic risk factors among people with diabetes.
Infl ammatory potential of the diet is associated with psychological stress in adults with type 2 diabetes: a methodological approach of e-Health
We studied the presence of psychological stress in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and if could be attributed to the consumption of a pro-inflammatory diet. We evaluated the inflammatory potential of the habitual Mexican diet, addressed by tools with an approach to collecting information on e-Health.
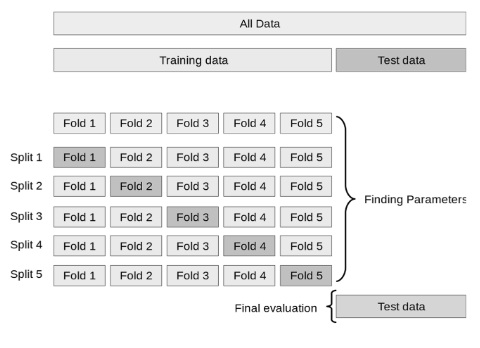
Multivariable prediction model of complications derived from diabetes mellitus using machine learning on scarce highly unbalanced data
Diabetes mellitus (DM) increases the risk complications in addition to mortality. Quantifying the risk of com- plications using artificial intelligence could be a way to design comprehensive patient healthcare programs
Risk factors associated with severity, prognosis, and evolution of patients with tropical diabetic hand syndrome
Tropical diabetic hand syndrome (TDHS) is rarely described and recognized in the literature as a complication in people with diabetes, and Mexico has high incidence rates of diabetes mellitus II (DMII). The minor or major amputation of the arm represents a physically and economically significant morbidity problem in patients.
Stepping up foot care: assessment over foot care knowledge and behavior among individuals with diabetes of risk levels
Diabetic foot is a global threat to public health, as it can lead to infections and amputations and cause significant pain and economic costs for patients. Diabetic foot patients in northern China have more severe local ulcers, worse prognosis, and longer disease duration.
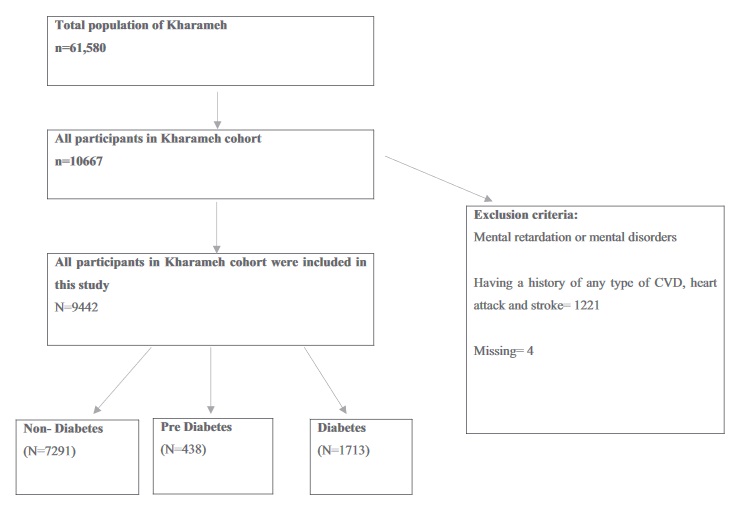
The effect of prediabetes and diabetes on the incidence of cardiovascular disease in the population of 40 to 70 years in the south of Iran: a population-based cohort study
Diabetes is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease. The purpose of this study was to explore the role of diabetes and prediabetes in the risk of cardiovascular disease.
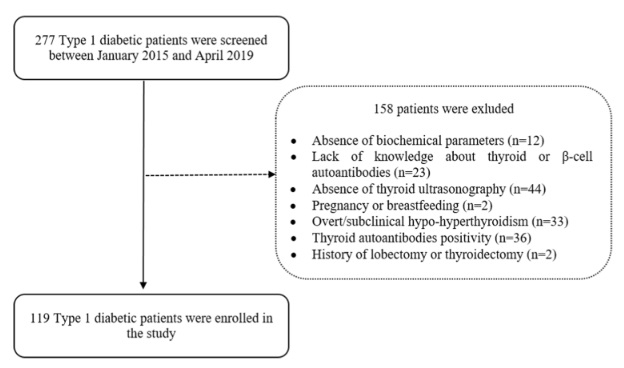
Prevalence of thyroid nodule and its association with β-cell autoantibodies in adult patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus without thyroid dysfunction
Although many studies have shown the relationship between type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and autoimmune thyroid diseases, few studies have conducted a morphological evaluation of the thyroid gland in T1DM without thyroid disease.
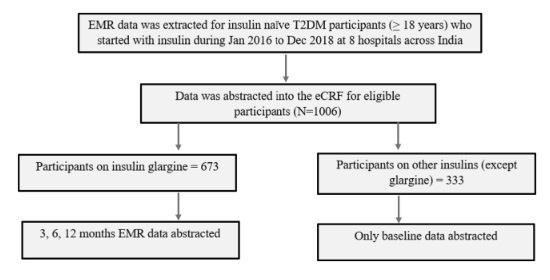
A retrospective electronic medical record-based study of insulin usage and outcomes in insulin-naive Indian adults with T2DM: The REALITY study
This retrospective longitudinal study analyzed the demographic profile, insulin usage pattern, and outcomes of insulin-naive adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who initiated insulin glargine.
Prevalence and associated factors of tenia pedis among patients with diabetes in Jordan
Diabetes mellitus is an etiological factor of tinea pedis (TP) which can increase the risk of diabetes-related foot complications. There is scarce research investigating the epidemiology of TP among patients with diabetes and this study contributed to filling this gap.
Evaluation of HbA1c levels as probable diagnostic of depression symptoms in Mexican individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
We evaluated the sociodemographic, anthropometric, and clinical features of Mexican individuals with clinical depressive symptoms in order to identify predictors for depression symptoms; finally, we evaluated if HbA1c levels could be used as a probable diagnostic of depressive symptoms in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
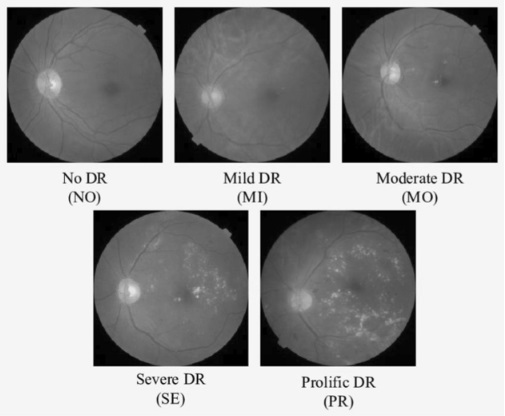
Classification of diabetic retinopathy severity level using deep learning
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is an eye disease developed due to long-term diabetes mellitus, which affects retinal damage. The treatment at the right time supports people in retaining vision, and the early detection of DR is the only solu- tion to prevent blindness.
Correlation of presence and severity of glucose derangements with severity of Liver Cirrhosis: a hospital-based cross sectional observational study from New Delhi
Association between liver cirrhosis (LC) and glucose intolerance has been known since long. Many studies in the past have attempted to explore the correlation of glucose metabolism disorders (GMD) with the severity of LC with mixed results (some favouring i.e. higher prevalence of GMD in more severe LC; others negating). This study was conducted to shed further light on the significance of this association.
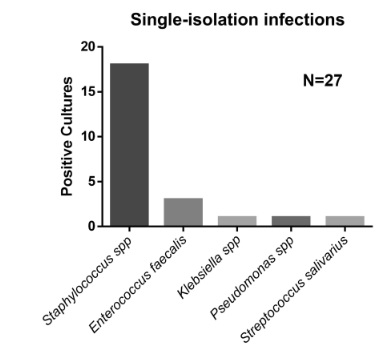
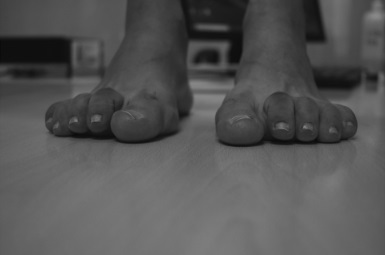
Severe limited joint mobility (LJM) involving both the hands and feet in type 1 diabetes mellitus
Limited joint mobility (LJM) is one of the most common disabling musculo-skeletal complications in long- standing diabetes. Though it has been described extensively in previous pieces of literature, symmetrical involvement of both upper and lower limbs hasn’t been much reported in recent accounts.
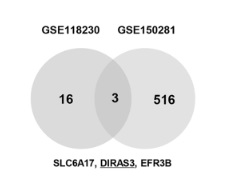
Silencing of DIRAS3 improves the proliferation and insulin secretion of palmitic acid-treated pancreatic β-cells through regulating PI3K/ AKT signaling
Type-2 diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterised by hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. This study aims to explore the role and mechanism of DIRAS family GTPase 3 (DIRAS3) in mediating pancreatic β-cell death and insulin secretion.
Impact of the supplementation of melatonin on oxidative stress marker and serum endothelin-1 in patients with metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is characterized by the cluster of risk factors associated with diabetes and cardio-vascular diseases. Given the influential role of oxidative stress (OxS) in the pathogenesis of MetS and the antioxidant properties of melatonin, our study aims to investigate the impact of melatonin supplementation on OxS biomarkers and serum endothelin-1 (ET-1) levels in patients diagnosed with MetS.
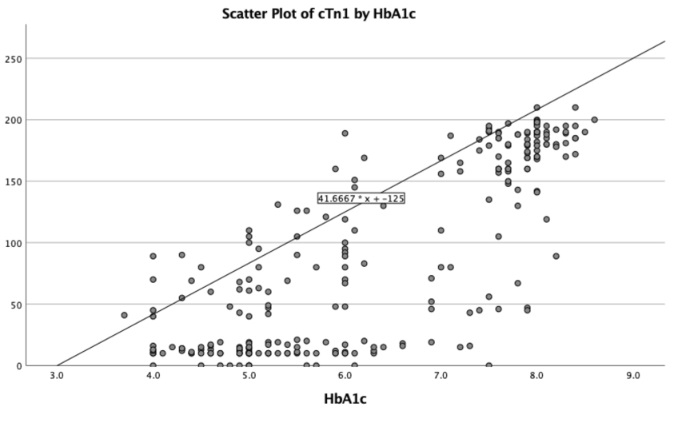
The association of HbA1C and cTnI with mortality and severity of disease among patients with acute coronary syndrome
In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the association of glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA 1 C) and cardiac troponin I levels (cTn1) with the 30-day mortality and severity of myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ACS.